Given a binary tree
1 | struct Node { |
Populate each next pointer to point to its next right node. If there is no next right node, the next pointer should be set to NULL.
Initially, all next pointers are set to NULL.
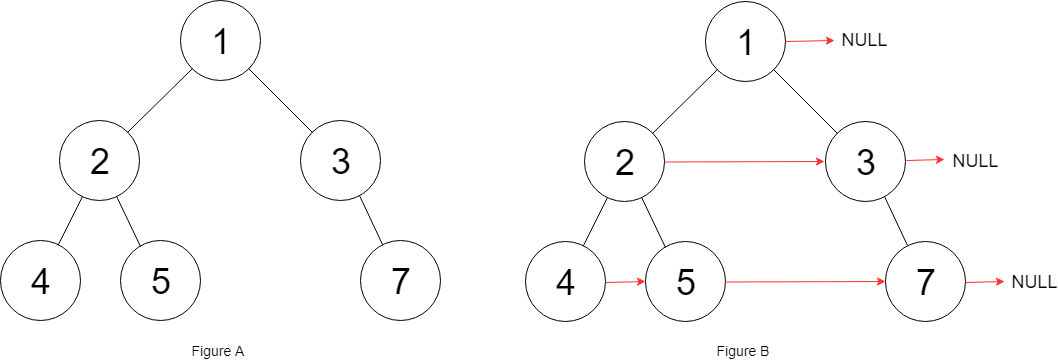
题目的大致要求就是这样,使用next指针指向右边的兄弟节点。
Note:
You may only use constant extra space.
Recursive approach is fine, implicit stack space does not count as extra space for this problem.
思路
其实,这个题就是将所有兄弟从左到右连接在一起的意思,所以,可以使用层次遍历的形式去完成。
同时,由于他也说了,使用栈的这种形式其实是不算是额外空间的,因此,使用递归也是可以的。递归也就是使用深度优先的方式去连接兄弟节点,不过,值得一提的是,因为,这是从左到右连接的兄弟节点,因此,递归的时候,要从右往左去建立连接,不然,是会出错的。
首先,有一点是需要统一的,无论是递归还是迭代,建立next节点都是需要依赖父节点的,也即是说,在遍历到父节点的时候,就需要为他的所有子节点建立好next的关系了。
1 | // Definition for a Node. |
不使用额外空间的层次遍历
其实,我们可以将树的每一层都看作是一个链表,而这个链表的头部则是一个存在于树之外的root节点。当我们要建立这个层次的关系的时候,其实就是,不断从这个链表的next节点插入新的值。
而root->next则总是指向当前层的第一个节点。那么,我们自然就可以得到一个从上往下,从左往右的层次遍历的关系了。
1 | Node* connect(Node* root) { |
使用栈
其实,使用栈的话,就比较简单明了了。
其实就是列举所有的方式,然后,去按情况连接next。
首先,假如父节点存在左孩子,若右孩子存在,则直接左右连接,否则,向node->next寻找,直到找到一个离他最近的节点,然后连接起来。
然后,就是加入存在右孩子,就向node->next找到离他最近的一个节点连接。
从右子树往左子树遍历,即可完成了。
1 |
|
题目来源
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node-ii